This is a guest article written by Reza Kalbasi, Director of New Zealand Geoanalytics Ltd on how HERA members could benefit from technologies in their business such as Geographical Information Systems (GIS).
Reza is a highly experienced GIS practitioner with over 15 years of experience with engineering firms like Aurecon, WSP Golder, and Harrison Grierson. He also has experience work in the government sector globally.
As a certified Geographic Information Systems Professional (Asia Pacific), GISP-AP, he is passionate about leveraging geospatial technology to drive innovation, business optimisation, and solve complex challenges.
What is Location Intelligence and why is it relevant to HERA members?
In the world of business, location matters.
Understanding the impact of location-based factors on operations is crucial for making informed decisions. That’s where Location Intelligence (LI) comes into play. LI harnesses the power of Geographic Information System (GIS) technology to provide businesses with spatial analysis and visualisation capabilities that unlock valuable insights.
The benefits from LI can be seen in several key areas:
- Market analysis and customer Insights: by visualising customer locations, demographics, and market trends, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behaviour, preferences, and target markets. Overlaying spatial data with customer data enables a deeper understanding of market dynamics.
- Sales territory optimisation and field service operations: optimising sales territories based on customer density, resource proximity, and travel time leads to increased productivity and customer satisfaction. GIS aids in scheduling field service operations and optimising routing for maintenance and repairs.
- Supply chain visualisation and analysis: mapping suppliers, warehouses, distribution centres, and transportation routes provides a comprehensive view of the supply chain. By analysing spatial data, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, optimise logistics, reduce costs, and enhance supply chain resilience.
-
Site selection: GIS plays a crucial role in identifying optimal locations for manufacturing facilities. By considering factors such as proximity to suppliers, transportation networks, labour markets, and environmental considerations, manufacturers can make informed decisions on new facility locations or expansions.
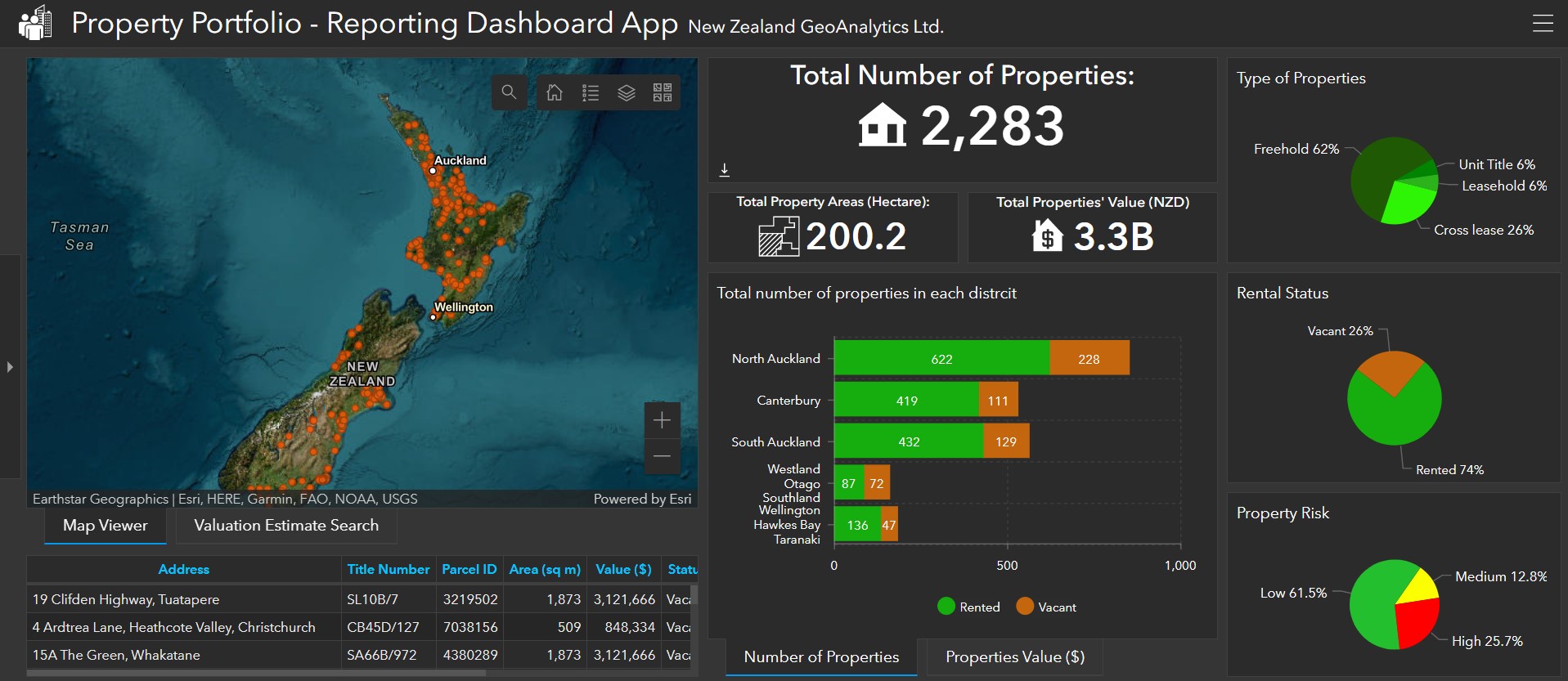
Additionally, GIS dashboards and reporting tools enable real-time monitoring of location-based projects, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), and facilitating proactive decision-making.
Integrating Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI) brings additional advantages. By combining GIS with AI and machine learning techniques, manufacturers can automate processes, optimise workflows, and improve quality control. GeoAI enables predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and optimisation models that enhance manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
The opportunities are endless. The most important thing is to get started.
What are the key differences between Business Intelligence and Location Intelligence?
While BI focuses on answering questions related to who, what, when, why, and how, LI adds the crucial “where” factor. LI incorporates location-related data into analysis, going beyond mapping to address forward-looking challenges.
The true value of location data lies in the details stored within your spreadsheets, including addresses, coordinates, project locations, and postcodes. While you can visualise points on a map using these data, the full benefits of Location Intelligence cannot be fully realised within your BI reports alone.
By leveraging LI, you can uncover meaningful insights hidden within your datasets. For instance, LI allows you to identify clusters or create heatmaps based on your data. This visual representation enables project managers and decision-makers to identify patterns and relationships within their datasets. They can gain a deeper understanding of their data and find answers to their questions more effectively.
Can you combine freely available data with company data to get increased insights?
Combining freely available data with company data enhances insights and decision-making. By integrating external datasets—demographics, market trends, geospatial, and environmental—with internal data, businesses gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations, customers, and market dynamics.
Uncovering patterns and correlations not apparent from internal data alone enables better product development, supply chain optimisation, risk assessment, and customer segmentation.
I will give you an example. One of our clients (a major pharmaceutical company) came to us asking for some help to clean their datasets so that they could link them with other publicly available data sets from the Ministry of Health or census data.
After listening to them explain the problem and seeing some sample data, it became apparent that they are limiting their options by thinking about their data as lists on excel spreadsheet. They were missing the fact that their data had a geographic location element to it, and if they would start to think of their data in the context of location it would be much easier to integrate with other data sources that are also location based, such as census data or Ministry of Health data.
So, we turned a simple data inquiry into an opportunity to experiment and learn about use of Location Intelligence and the end result is a dashboard that is loved and used by people in the field, as well as a new capability that our client now has to amplify its business intelligence with location intelligence.
However, when it comes to combining data sources, it’s very important to consider data privacy and security. Compliance with regulations and implementing data governance practices safeguard sensitive information.
What about GIS and BIM combined, is that possible?
Absolutely!
Combining GIS and BIM brings significant benefits to the construction and infrastructure industries:
- Enhanced planning and design: GIS-BIM integration allows better site analysis, visualising infrastructure within its geographic context, and improving decision-making during project planning and design.
- Improved asset management: Linking geospatial data from GIS with BIM models enables accurate asset tracking, real-time visualisation of asset status, and streamlined maintenance, reducing costs and enhancing performance.
- Advanced spatial analysis: Integrating GIS and BIM facilitates spatial relationship analysis, assessing the impact of projects on the surrounding environment, optimising design, and mitigating conflicts.
- Collaborative communication: GIS-BIM integration enhances collaboration among stakeholders, enabling seamless data sharing and coordination for better project outcomes.
- Efficient facilities management: The combination of GIS and BIM streamlines facilities management, optimising resource allocation, and improving operational efficiency.
- Spatial data infrastructure: GIS-BIM integration contributes to the development of spatial data infrastructure, enhancing data interoperability and supporting data-driven decision-making.
The integration of GIS and BIM revolutionises project processes, improves collaboration, and maximises the value of geospatial and building information.
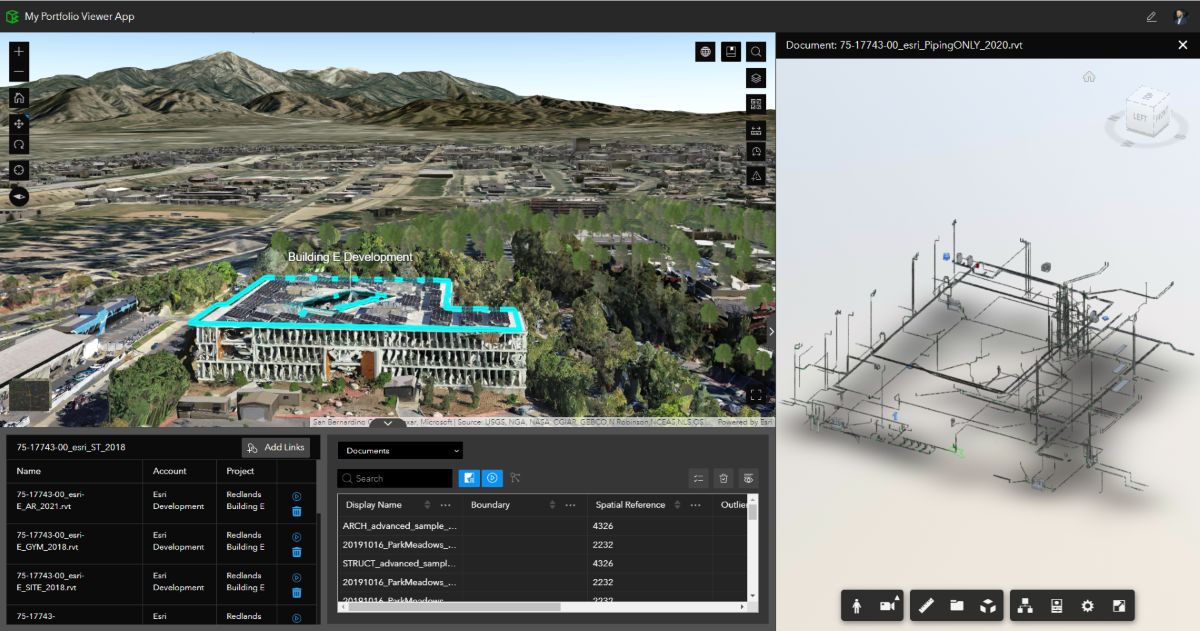
Has GIS influenced the way Aotearoa New Zealand industry operates?
Yes – and significantly so! Access to diverse GIS datasets from organisations and authorities, improved spatial analysis and planning, enhanced asset management, revolutionised emergency management, valuable customer insights, sustainable resource management, improved collaboration are just a few ways GIS has made an impact.
What are some valuable trends coming through in GIS right now and what will be next?
Looking ahead, emerging trends in GIS include workflow automation, spatial analysis advancements, data integration, geospatial insights, and mobile GIS data collection. These trends provide organisations with new opportunities to leverage spatial data, advanced analytics, and automation to gain insights and make data-driven decisions.
The future of GIS holds exciting possibilities, such as IoT integration for real-time data, 3D GIS and augmented reality for immersive visualisation, GeoAI for intelligent analysis, and big data analytics to handle large and complex datasets.
Exploring the potential of GIS and LI will unlock enhanced insights, optimise processes, and drive innovation. I predict that LI will become a strategic tool shaping the future of industries in Aotearoa.
Interested to know more?
As you know, HERA is very focused on our members innovating in their business for future success. Industry 4.0 technologies are also an area in which we are exploring more deeply to create opportunities for optimisation, increase productivity and similar in business models.
Moving forward, we hope to partner with IMS Projects and their connections such as Reza, to bring you more insights into future technologies, innovations and training that might help our members to stay ahead of the curve.
If this thought piece on harnessing the power of Location Intelligence to propel your operations to new heights resonated with you – you should certainly look deeper in to discovering the untapped potential that lies within your spatial data and embrace the opportunities presented by GIS. You can do so, by getting in touch for more information or an informal conversation at: insights@ims-projects.co.nz.

